
The Civil War was the deadliest military conflict in American history. The technology and brutality foreshadowed the coming World Wars.

Curated/Reviewed by Matthew A. McIntosh
Public Historian
Brewminate
Introduction
Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery’s expansion, won the 1860 U.S. presidential election. Seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln’s victory by seceding from the United States and forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. The war began on April 12, 1861, when the Confederacy bombarded Fort Sumter in South Carolina. A wave of enthusiasm for war swept over both North and South, as military recruitment soared. Four more southern states seceded after the war began and, led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, the Confederacy asserted control over about a third of the U.S. population in eleven states. Four years of intense combat, mostly in the South, ensued.
The Civil War is one of the most extensively studied and written about episodes in U.S. history. It remains the subject of cultural and historiographical debate. Of particular interest is the persisting myth of the Lost Cause of the Confederacy. The American Civil War was among the first wars to use industrial warfare. Railroads, the electric telegraph, steamships, the ironclad warship, and mass-produced weapons were all widely used during the war. In total, the war left between 620,000 and 750,000 soldiers dead, along with an undetermined number of civilian casualties, making the Civil War the deadliest military conflict in American history. The technology and brutality of the Civil War foreshadowed the coming World Wars.
1861 – Secession to Blockades
January 1861 – The South Secedes

When Abraham Lincoln, a known opponent of slavery, was elected president, the South Carolina legislature perceived a threat. Calling a state convention, the delegates voted to remove the state of South Carolina from the union known as the United States of America. The secession of South Carolina was followed by the secession of six more states—Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas–and the threat of secession by four more—Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. These eleven states eventually formed the Confederate States of America.
February 1861 – The South Creates a Government
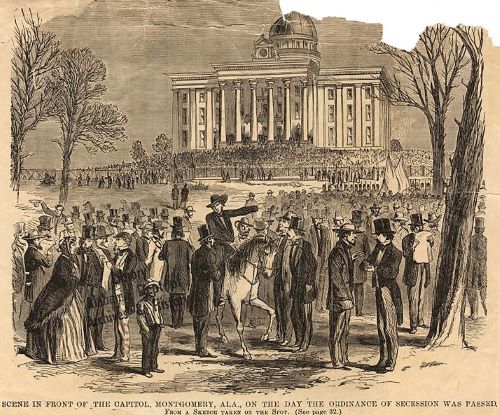

At a convention in Montgomery, Alabama, the seven seceding states created the Confederate Constitution, a document similar to the United States Constitution, but with greater stress on the autonomy of each state. Jefferson Davis was named provisional president of the Confederacy until elections could be held.
February 1861 – The South Seizes Federal Forts

When President Buchanan—Lincoln’s predecessor—refused to surrender southern federal forts to the seceding states, southern state troops seized them. At Fort Sumter, South Carolina troops repulsed a supply ship trying to reach federal forces based in the fort. The ship was forced to return to New York, its supplies undelivered.
March 1861 – Lincoln’s Inauguration

At Lincoln’s inauguration on March 4, the new president said he had no plans to end slavery in those states where it already existed, but he also said he would not accept secession. He hoped to resolve the national crisis without warfare.
April 1861 – Attack on Fort Sumter

When President Lincoln planned to send supplies to Fort Sumter, he alerted the state in advance, in an attempt to avoid hostilities. South Carolina, however, feared a trick; the commander of the fort, Robert Anderson, was asked to surrender immediately. Anderson offered to surrender, but only after he had exhausted his supplies. His offer was rejected, and on April 12, the Civil War began with shots fired on the fort. Fort Sumter eventually was surrendered to South Carolina.
April 1861 – Four More States Join the Confederacy
The attack on Fort Sumter prompted four more states to join the Confederacy. With Virginia’s secession, Richmond was named the Confederate capitol.
June 1861 – West Virginia Is Born
Residents of the western counties of Virginia did not wish to secede along with the rest of the state. This section of Virginia was admitted into the Union as the state of West Virginia on June 20, 1863.
June 1861 – Four Slave States Stay in the Union
Despite their acceptance of slavery, Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, and Missouri did not join the Confederacy. Although divided in their loyalties, a combination of political maneuvering and Union military pressure kept these states from seceding.
July 1861 – First Battle of Bull Run

Public demand pushed General-in-Chief Winfield Scott to advance on the South before adequately training his untried troops. Scott ordered General Irvin McDowell to advance on Confederate troops stationed at Manassas Junction, Virginia. McDowell attacked on July 21, and was initially successful, but the introduction of Confederate reinforcements resulted in a Southern victory and a chaotic retreat toward Washington by federal troops.
July 1861 – General McDowell Is Replaced
Suddenly aware of the threat of a protracted war and the army’s need for organization and training, Lincoln replaced McDowell with General George B. McClellan.
July 1861 – A Blockade of the South
To blockade the coast of the Confederacy effectively, the federal navy had to be improved. By July, the effort at improvement had made a difference and an effective blockade had begun. The South responded by building small, fast ships that could outmaneuver Union vessels.
On November 7, 1861, Captain Samuel F. Dupont’s warships silenced Confederate guns in Fort Walker and Fort Beauregard. This victory enabled General Thomas W. Sherman’s troops to occupy first Port Royal and then all the famous Sea Islands of South Carolina, where Timothy H. O’Sullivan recorded them making themselves at home.
1862 – Water to Land
January 1862 – Abraham Lincoln Takes Action
On January 27, President Lincoln issued a war order authorizing the Union to launch a unified aggressive action against the Confederacy. General McClellan ignored the order.
March 1862 – Mclelland Loses Command

On March 8, President Lincoln—impatient with General McClellan’s inactivity—issued an order reorganizing the Army of Virginia and relieving McClellan of supreme command. McClellan was given command of the Army of the Potomac, and ordered to attack Richmond. This marked the beginning of the Peninsular Campaign.
March 1862 – Battle of the “Monitor” and the “Merrimac”

In an attempt to reduce the North’s great naval advantage, Confederate engineers converted a scuttled Union frigate, the U.S.S. Merrimac, into an iron-sided vessel rechristened the C.S.S. Virginia. On March 9, in the first naval engagement between ironclad ships, the Monitor fought the Virginia to a draw, but not before the Virginia had sunk two wooden Union warships off Norfolk, Virginia.
April 1862 – The Battle of Shiloh
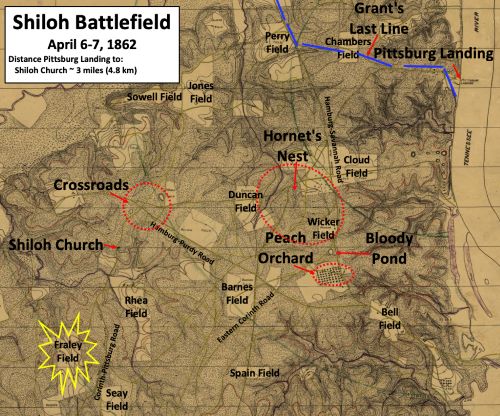
On April 6, Confederate forces attacked Union forces under General Ulysses S. Grant at Shiloh, Tennessee. By the end of the day, the federal troops were almost defeated. Yet, during the night, reinforcements arrived, and by the next morning the Union commanded the field. When Confederate forces retreated, the exhausted federal forces did not follow. Casualties were heavy—13,000 out of 63,000 Union soldiers died, and 11,000 of 40,000 Confederate troops were killed.
General Quincy A. Gillmore battered Fort Pulaski, the imposing masonry structure near the mouth of the Savannah River, into submission in less than two days, (April 10-11, 1862). His work was promptly recorded by the indefatigable Timothy H. O’Sullivan.
April 1862 – New Orleans
Flag Officer David Farragut led an assault up the Mississippi River. By April 25, he was in command of New Orleans.
April 1862 – The Peninsular Campaign
In April, General McClellan’s troops left northern Virginia to begin the Peninsular Campaign. By May 4, they occupied Yorktown, Virginia. At Williamsburg, Confederate forces prevented McClellan from meeting the main part of the Confederate army, and McClellan halted his troops, awaiting reinforcements.
May 1862 – “Stonewall” Jackson Defeats Union Forces

Confederate General Thomas J. “Stonewall” Jackson, commanding forces in the Shenandoah Valley, attacked Union forces in late March, forcing them to retreat across the Potomac. As a result, Union troops were rushed to protect Washington, D.C.
June 1862 – The Battle of Seven Pines (Fair Oaks)
On May 31, the Confederate army attacked federal forces at Seven Pines, almost defeating them; last-minute reinforcements saved the Union from a serious defeat. Confederate commander Joseph E. Johnston was severely wounded, and command of the Army of Northern Virginia fell to Robert E. Lee.
July 1862 – The Seven Days’ Battles
Between June 26 and July 2, Union and Confederate forces fought a series of battles: Mechanicsville (June 26-27), Gaines’s Mill (June 27), Savage’s Station (June 29), Frayser’s Farm (June 30), and Malvern Hill (July 1). On July 2, the Confederates withdrew to Richmond, ending the Peninsular Campaign.
July 1862 – A New Commander of the Union Army

On July 11, Major-General Henry Halleck was named general-in-chief of the Union army.
August 1862 – Pope’s Campaign
Union General John Pope suffered defeated at the Second Battle of Bull Run on August 29-30. General Fitz-John Porter was held responsible for the defeat because he had failed to commit his troops to battle quickly enough; he was forced out of the army by 1863.
September 1862 – Harper’s Ferry

Union General McClellan defeated Confederate General Lee at South Mountain and Crampton’s Gap in September, but did not move quickly enough to save Harper’s Ferry, which fell to Confederate General Jackson on September 15, along with a great number of men and a large body of supplies.
September 1862 – Antietam
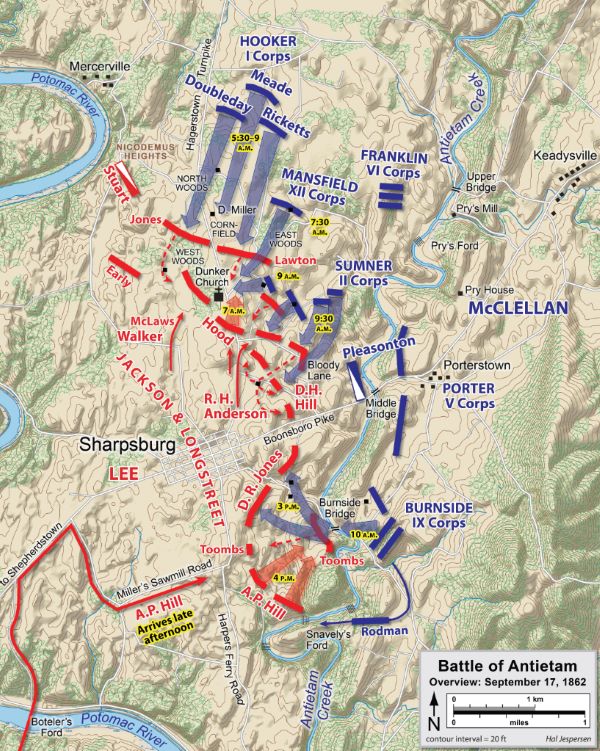
On September 17, Confederate forces under General Lee were caught by General McClellan near Sharpsburg, Maryland. This battle proved to be the bloodiest day of the war; 2,108 Union soldiers were killed and 9,549 wounded—2,700 Confederates were killed and 9,029 wounded. The battle had no clear winner, but because General Lee withdrew to Virginia, McClellan was considered the victor. The battle convinced the British and French—who were contemplating official recognition of the Confederacy—to reserve action, and gave Lincoln the opportunity to announce his Preliminary Emancipation Proclamation (September 22), which would free all slaves in areas rebelling against the United States, effective January 1, 1863.
The Army of the Potomac remained in possession of the field, and the photographers were able to work over it thoroughly immediately after the battle of September 17. One can witness President Lincoln’s visit to McClellan’s headquarters, and follow the army across the Potomac at Berlin (present day Brunswick, Maryland) and into re-occupied Harper’s Ferry.
December 1862 – The Battle of Fredericksburg

General McClellan’s slow movements, combined with General Lee’s escape, and continued raiding by Confederate cavalry, dismayed many in the North. On November 7, Lincoln replaced McClellan with Major-General Ambrose E. Burnside. Burnside’s forces were defeated in a series of attacks against entrenched Confederate forces at Fredericksburg, Virginia, and Burnside was replaced with General Joseph Hooker.
1863 – Emancipation to Chattanooga
January 1863 – Emancipation Proclamation

In an effort to placate the slave-holding border states, Lincoln resisted the demands of radical Republicans for complete abolition. Yet some Union generals, such as General B. F. Butler, declared slaves escaping to their lines “contraband of war,” not to be returned to their masters. Other generals decreed that the slaves of men rebelling against the Union were to be considered free. Congress, too, had been moving toward abolition. In 1861, Congress had passed an act stating that all slaves employed against the Union were to be considered free. In 1862, another act stated that all slaves of men who supported the Confederacy were to be considered free. Lincoln, aware of the public’s growing support of abolition, issued the Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863, declaring that all slaves in areas still in rebellion were, in the eyes of the federal government, free.
March 1863 – The First Conscription Act
Because of recruiting difficulties, an act was passed making all men between the ages of 20 and 45 liable to be called for military service. Service could be avoided by paying a fee or finding a substitute. The act was seen as unfair to the poor, and riots in working-class sections of New York City broke out in protest. A similar conscription act in the South provoked a similar reaction.
May 1863 – The Battle of Chancellorsville

On April 27, Union General Hooker crossed the Rappahannock River to attack General Lee’s forces. Lee split his army, attacking a surprised Union army in three places and almost completely defeating them. Hooker withdrew across the Rappahannock River, giving the South a victory, but it was the Confederates’ most costly victory in terms of casualties.
May 1863 – The Vicksburg Campaign

Union General Grant won several victories around Vicksburg, Mississippi, the fortified city considered essential to the Union’s plans to regain control of the Mississippi River. On May 22, Grant began a siege of the city. After six weeks, Confederate General John Pemberton surrendered, giving up the city and 30,000 men. The capture of Port Hudson, Louisiana, shortly thereafter placed the entire Mississippi River in Union hands. The Confederacy was split in two.
June-July 1863 – The Gettysburg Campaign
Confederate General Lee decided to take the war to the enemy. On June 13, he defeated Union forces at Winchester, Virginia, and continued north to Pennsylvania. General Hooker, who had been planning to attack Richmond, was instead forced to follow Lee. Hooker, never comfortable with his commander, General Halleck, resigned on June 28, and General George Meade replaced him as commander of the Army of the Potomac.
On July 1, a chance encounter between Union and Confederate forces began the Battle of Gettysburg. In the fighting that followed, Meade had greater numbers and better defensive positions. He won the battle, but failed to follow Lee as he retreated back to Virginia. Militarily, the Battle of Gettysburg was the high-water mark of the Confederacy; it is also significant because it ended Confederate hopes of formal recognition by foreign governments. On November 19, President Lincoln dedicated a portion of the Gettysburg battlefield as a national cemetery, and delivered his memorable “Gettysburg Address.”
September 1863 – The Battle of Chickamauga

On September 19, Union and Confederate forces met on the Tennessee-Georgia border, near Chickamauga Creek. After the battle, Union forces retreated to Chattanooga, and the Confederacy maintained control of the battlefield.
After the Battle of Gettysburg, General Meade engaged in some cautious and inconclusive operations, but the heavy activity of the photographers was confined to the intervals between them—at Bealeton, southwest of Warrenton, in August, and at Culpeper, before the Mine Run Campaign.
November 1863 – The Battle of Chattanooga and Siege of Knoxville
On November 23-25, Union forces pushed Confederate troops away from Chattanooga. The victory set the stage for General Sherman’s Atlanta Campaign.
After Rosecrans’s debacle at Chickamauga, September 19-20, 1863, Confederate General Braxton Bragg’s army occupied the mountains that ring the vital railroad center of Chattanooga. Grant, brought in to save the situation, steadily built up offensive strength, and on November 23- 25 burst the blockade in a series of brilliantly executed attacks.
The difficult strategic situation of the federal armies after Chickamauga enabled Bragg to detach a force under Longstreet to drive Burnside out of eastern Tennessee. Burnside sought refuge in Knoxville, which he successfully defended from Confederate assaults.
1864 – Brandy Station to Nashville
January-April 1864 – Winter Quarters at Brandy Station

All was quiet beyond the Rappahannock, but there was a rich harvest for the photographers. Some photographs date from December 1863.
May 1864 – Grant’s Wilderness Campaign
General Grant, promoted to commander of the Union armies, planned to engage Lee’s forces in Virginia until they were destroyed. North and South met and fought in an inconclusive three-day battle in the Wilderness. Lee inflicted more casualties on the Union forces than his own army incurred, but unlike Grant, he had no replacements.
May 1864 – The Battle of Spotsylvania
General Grant continued to attack Lee. At Spotsylvania Court House, he fought for five days, vowing to fight all summer if necessary.
June 1864 – The Battle of Cold Harbor
Grant again attacked Confederate forces at Cold Harbor, losing over 7,000 men in twenty minutes. Although Lee suffered fewer casualties, his army never recovered from Grant’s continual attacks. This was Lee’s last clear victory of the war.
June 1864 – The Siege of Petersburg

Grant hoped to take Petersburg, below Richmond, and then approach the Confederate capital from the south. The attempt failed, resulting in a ten month siege and the loss of thousands of lives on both sides.
General Benjamin F. Butler’s command was in the vacinity of Petersburg as early as May 11, missing its opportunity to capture this vital railroad center; but the photographs are all from the later days when Butler was holding a fortified line on both sides of the James and extending nothward as far as the Market or River Road running into Richmond. The photographs follow Butler’s lines from south to north, and then, after the evacuation of Richmond, record the Confederate defenses on the James.
July 1864 – Confederate Troops Approach Washington, D.C.
Confederate General Jubal Early led his forces into Maryland to relieve the pressure on Lee’s army. Early got within five miles of Washington, D.C., but on July 13, he was driven back to Virginia.
August 1864 – General William T. Sherman’s Atlanta Campaign
Union General Sherman departed Chattanooga, and was soon met by Confederate General Joseph Johnston. Skillful strategy enabled Johnston to hold off Sherman’s force—almost twice the size of Johnston’s. However, Johnston’s tactics caused his superiors to replace him with General John Bell Hood, who was soon defeated. Hood surrendered Atlanta, Georgia, on September 1; Sherman occupied the city the next day. The fall of Atlanta greatly boosted Northern morale.
November 1864 – General William T. Sherman’s March to the Sea

General Sherman continued his march through Georgia to the sea. In the course of the march, he cut himself off from his source of supplies, planning for his troops to live off the land. His men cut a path 300 miles in length and 60 miles wide as they passed through Georgia, destroying factories, bridges, railroads, and public buildings.
After three and a half months of incessant maneuvering and much hard fighting, Sherman forced Hood to abandon Atlanta, the munitions center of the Confederacy. Sherman remained there, resting his war-worn men and accumulating supplies, for nearly two-and-a-half months.
November 1864 – Abraham Lincoln Is Re-Elected
The Republican party nominated President Abraham Lincoln as its presidential candidate, and Andrew Johnson for vice-president. The Democratic party chose General George B. McClellan for president, and George Pendleton for vice-president. At one point, widespread war-weariness in the North made a victory for Lincoln seem doubtful. In addition, Lincoln’s veto of the Wade-Davis Bill—requiring the majority of the electorate in each Confederate state to swear past and future loyalty to the Union before the state could officially be restored—lost him the support of Radical Republicans who thought Lincoln too lenient. However, Sherman’s victory in Atlanta boosted Lincoln’s popularity and helped him win re-election by a wide margin.
December 1864 – Fort Monroe and Hampton, Virginia
Its own intrinsic strength and the ease with which it could be supplied and reinforced by sea kept the largest American fort in federal hands throughout the war. Fort Monroe was the starting point for McClellan’s Peninsular Campaign in 1862 and for Butler’s advance to Petersburg in 1864.
December 1864 – Sherman at the Sea
After marching through Georgia for a month, Sherman stormed Fort McAllister on December 13, 1864, and captured Savannah itself eight days later.
December 1864 – Hood before Nashville
Continuing his policy of taking the offensive at any cost, General John B. Hood brought his reduced army before the defenses of Nashville, where it was repulsed by General George H. Thomas on December 15-16, in the most complete victory of the war.
1865 – Fort Fisher to Confederate Surrender
January 1865 – Fort Fisher

After Admiral David D. Porter’s squadron of warships had subjected Fort Fisher to a terrific bombardment, General Alfred H. Terry’s troops took it by storm on January 15, and Wilmington, North Carolina, the last resort of the blockade-runners, was sealed off.
January 1865 – The Fall of the Confederacy
Transportation problems and successful blockades caused severe shortages of food and supplies in the South. Starving soldiers began to desert Lee’s forces, and although President Jefferson Davis approved the arming of slaves as a means of augmenting the shrinking army, the measure was never put into effect.
February 1865 – Sherman Marches through North and South Carolina
Union General Sherman moved from Georgia through South Carolina, destroying almost everything in his path.
February 1865 – A Chance for Reconciliation Is Lost
Confederate President Jefferson Davis agreed to send delegates to a peace conference with President Lincoln and Secretary of State William Seward, but insisted on Lincoln’s recognition of the South’s independence as a prerequisite. Lincoln refused, and the conference never occurred.
On March 25, General Lee attacked General Grant’s forces near Petersburg, but was defeated—attacking and losing again on April 1. On April 2, Lee evacuated Richmond, the Confederate capital, and headed west to join with other forces.
April 1865 – Surrender at Appomattox Courthouse

General Lee’s troops were soon surrounded, and on April 7, Grant called upon Lee to surrender. On April 9, the two commanders met at Appomattox Courthouse, and agreed on the terms of surrender. Lee’s men were sent home on parole—soldiers with their horses, and officers with their side arms. All other equipment was surrendered.
April 1865 – The Assassination of President Lincoln
On April 14, as President Lincoln was watching a performance of “Our American Cousin” at Ford’s Theater in Washington, D.C., he was shot by John Wilkes Booth, an actor from Maryland obsessed with avenging the Confederate defeat. Lincoln died the next morning. Booth escaped to Virginia. Eleven days later, cornered in a burning barn, Booth was fatally shot by a Union soldier. Nine other people were involved in the assassination; four were hanged, four imprisoned, and one acquitted.
April-May 1865 – Final Surrenders among Remaining Confederate Troops
Remaining Confederate troops were defeated between the end of April and the end of May. Jefferson Davis was captured in Georgia on May 10.
November 1865 – The Execution of Captain Henry Wirz
The notorious superintendent of the Confederate prison at Andersonville, Georgia, was tried by a military commission presided over by General Lew Wallace from August 23 to October 24, 1865, and was hanged in the yard of the Old Capitol Prison on November 10.
Originally published by the United States Library of Congress to the public domain.






